Any internet-enabled device has a unique IP address that identifies it for internet communication to work. These IP addresses can be IPv4 or IPv6, or both since both methods are in place today. Because IPv4 is more common, people often consider it the sole IP address for any device, focusing all methods on modifying this address only. However, there can be numerous situations where you need to disable IPv6 discretely.
But how to disable IPv6, we hear you ask. Don’t worry; this quick guide explains it for all major operating systems step-by-step. But before that, let’s quickly understand what IPv6 is all about and which factors trigger the need to disable IPv6.
What is IPV6?
The IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6) is the newest internet protocol that identifies devices and networks across the internet. It emerged as a solution to the rising IPv4 exhaustion in response to the growing number of devices connecting to the internet.
Technically, IPv6 uses 128-bit internet addresses, unlike IPv4, which relies on 32-bit addresses. Thus, it can handle more unique IP numbers than the existing IPv4. In addition, IPv6 provides better security, improved network address translation, and administrative workload. Besides, it eliminates the dependency on location (unlike IPv4) by retaining the same unique IP address for a device regardless of the physical location.
Why should I disable IPv6?
Although, IPv6 generally works well with the prevalent IPv4. But it may also cause conflicts under certain circumstances, requiring you to disable it.
For instance, it may create network issues or cause VPN leaks when you wish to hide your actual online location and IP address. Unfortunately, many robust VPNs, including NordVPN or Surfshark, still do not support IPv6. So, while they offer advanced IP leak protection, you may still have to disable IPv6 manually to prevent accidental exposure of your actual IP address online.
Similarly, if your internet connection reconnects repeatedly, it may be your router closing the connection due to an IPv6 conflict.
Such problems arise because of the poor adaptation of IPv6 at the end-user level. Also, some ISPs, like AT&T, Verizon, and Xfinity, are still struggling with adequate adaptation and implementation of IPV6. So, to avoid all these problems, you may have to decide about disabling IPv6 on your device.
So, to avoid all these problems, you may have to decide about disabling IPv6 on your device.
Disable IPv6 on Windows 10
1. Go to the bottom-right corner of your screen and right-click on the ‘Network/Wi-Fi’ icon. A pop-up menu will appear, as shown below.
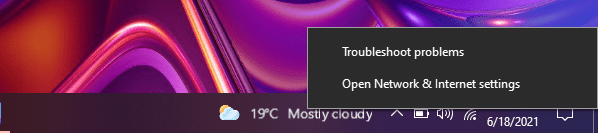
2. Click on the ‘Open Network & Internet settings‘ option. Then, the following setting dialog would appear on your screen.
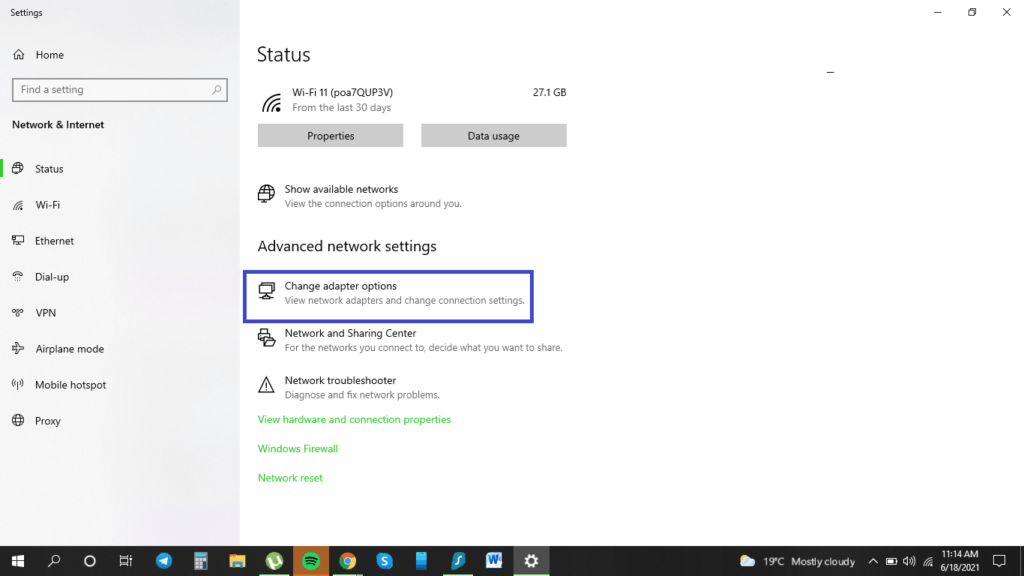
3. Click on the ‘Change adapter options‘ setting (highlighted in the picture above). A list of the available network adaptors will appear.

4. Now, right-click on the active network adapter and select ‘Properties.’
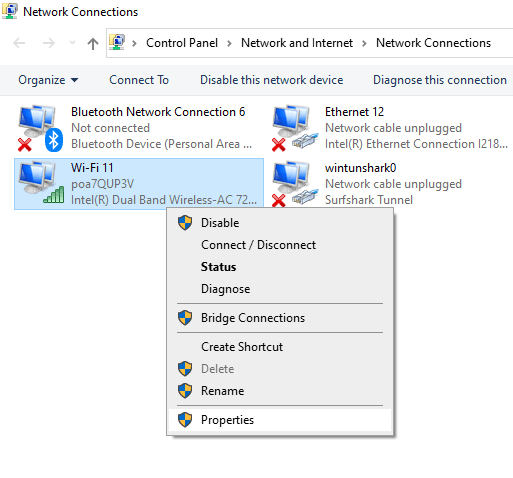
5. A pop-up window will open. Scroll down to find the ‘Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6)‘ option.
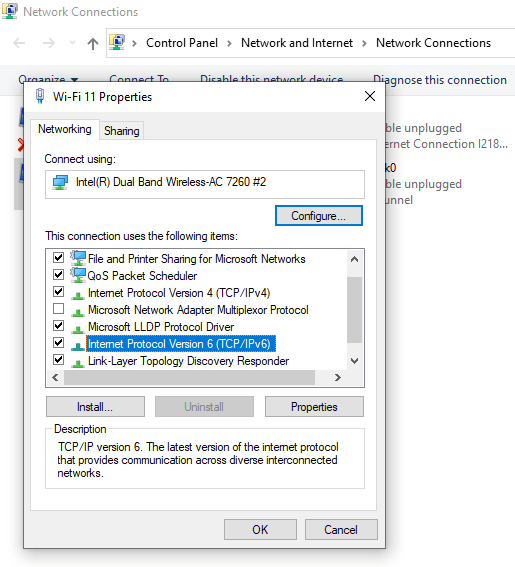
6. You may likely find this setting already checked. Click the checkbox to uncheck it and tap ‘OK‘ to save the changes.
7. Restart your computer to apply the changes.
Disable IPv6 on macOS X
Follow the steps below to disable IPv6 on your macOS X device.
1. Click ‘System Preferences‘ and tap on the ‘Network‘ icon.
2. Choose the active network.
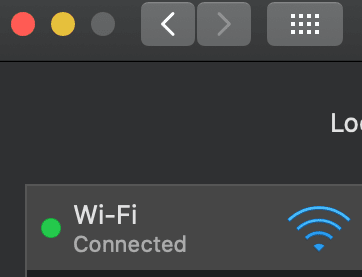
3. Click on the ‘Advanced…’ button.

4. Tap on the ‘TCP/IP‘ tab.
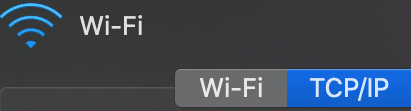
5. On the drop-down menu, select ‘Configure IPv6‘ and set it to ‘Link-local only.’ (If you do not find this setting, see if your system gives you the ‘Off‘ option in the drop-down menu. If yes, then select ‘Off.’)
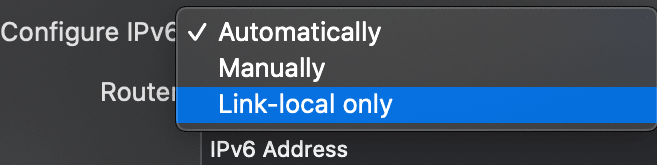
6. Click the ‘OK‘ button and restart your device.
Disable IPv6 on Spectrum router
If you use a rac2v1k Spectrum router, it is straightforward to disable IPv6 through the web interface.
1. Sign in to the router’s admin panel using the given credentials. (You will find the URL for the web interface and the login password at the back of the router. Most routers have ‘http://192.168.1.1‘ as the dashboard URL and ‘admin‘ as both the username and the password.)
2. Tap on the ‘Advanced‘ button and click ‘IPv6.’
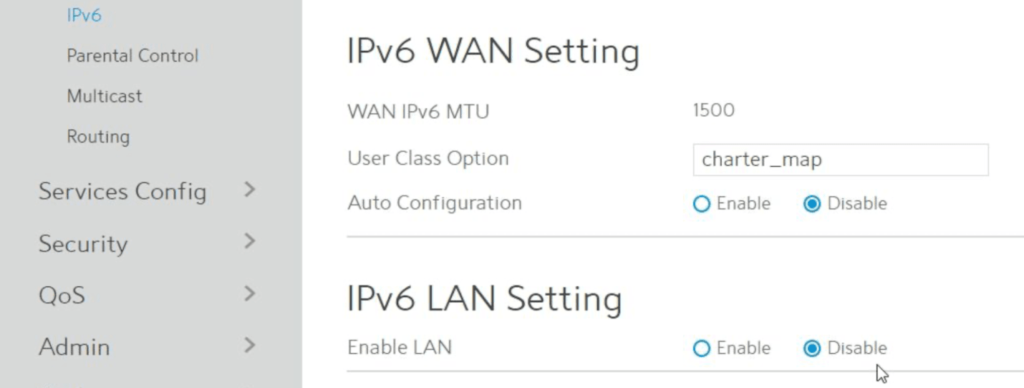
3. Select ‘Disable‘ under the settings and finish with ‘Apply.’
Disable IPv6 on other routers
Do the following to disable IPv6 on your router. (These steps generally apply to all routers; though, you may find some changes in wordings in the case of your specific router model.)
1. First, you need to find your router’s gateway address. It will enable you to connect to your router and log in. Here’s how to get your default gateway.
- Open the ‘Run‘ command box. (Press the Windows button plus the letter ‘R‘ on your keyboard.)
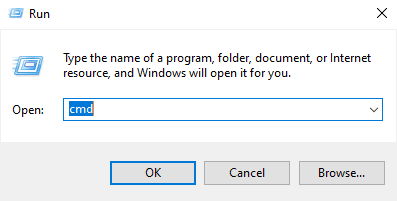
- On the small window that appears, type ‘cmd‘ and then hit ‘OK.’
- Now, the command prompt will appear (like the picture below illustrates).
- Type the word ‘ipconfig‘ and then press the ‘Enter‘ button on your keyboard.
- You’ll now get your default getaway information (as highlighted in the image below).
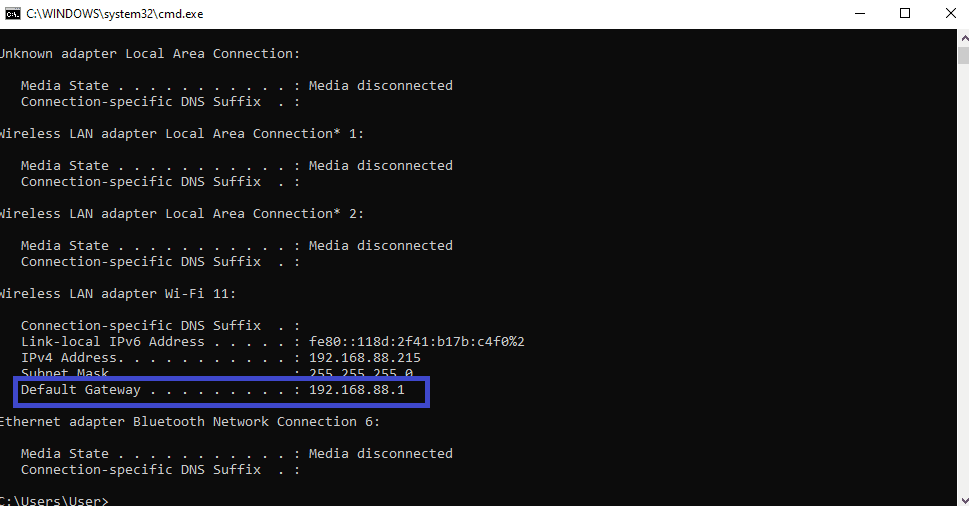
2. Copy and paste the default gateway on your browser.
3. A window will pop up that prompts you to sign in.
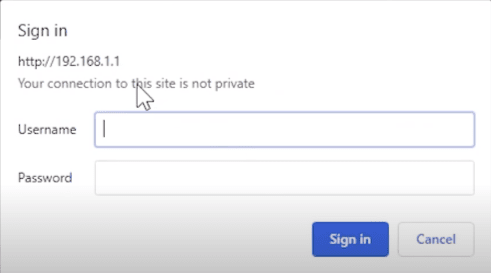
4. Put in your login credentials (find the information at the back bottom of your router) to get into your router.
5. Click on the ‘Settings‘ menu. Then go to the ‘Advanced settings‘ and scroll down to IPv6. (Note that the interface will vary depending on your router and Internet Service Provider (ISP).)
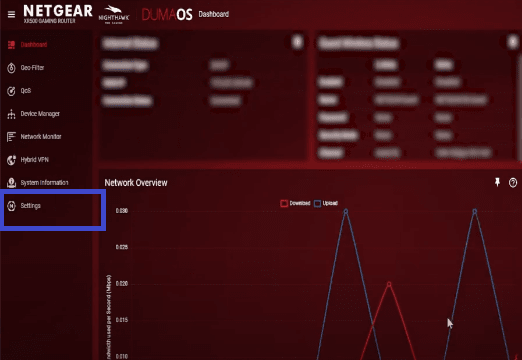
6. Under IPv6 settings, click ‘Disable‘ on the internet connection type.

7. This is it. Your router will now be on IPv4 only.
Why keeping IPv6 turned on might be a good idea
Recently, disabling IPv6 on devices has raised concerns. According to Microsoft, you should keep IPv6 enabled with an option to prefer IPv4.
However, since you’re reading this guide, you might have some apprehensions about the potential privacy issues with keeping IPv6 enabled.
So now, the question arises, ‘should you transition from IPv4 to IPv6?’ Let’s understand.
Microsoft has marked IPv6 as necessary for smoothly running Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, and the subsequent Windows versions. It says that without IPv6, many features will not work correctly.
So, how would Windows use IPv6 if your router does not support it and your Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server only offers IPv4?
Most devices and networks worldwide use IPv4 addresses, although IPv6 is the latest protocol. Understand that your DHCP will use IPv4 because of compatibility but still access the internet with IPv6.
Hence, you should not deactivate IPv6 completely. Instead, consider using both of them. For example, you can use IPv4 for easier readability while allowing Windows to choose IPv6.
So, although the Windows operating system depends on IPv6 and Microsoft cannot do any testing if it is deactivated. Nonetheless, some things may function behind the scenes. But the OS will have to look for outdated protocols if IPv6 isn’t available.
In the days of Windows 7, many routers did not support IPv6. Activating it could cause your internet connection to lag. However, when Windows 8 and Server 2012 were introduced, the OS would automatically choose IPv4 if IPv6 was not working. It did not require any configuration or disabling.
A quick look at the benefits of keeping IPv6 enabled
IPv4 is one of the oldest technologies in computers. But, when it was created, there weren’t many computers, and security was not even necessary. (Do you know IPv4 didn’t have in-built security?)
However, things have changed, and security is a top priority for IPv6.
Here are some of the IPv6 advantages.
- You won’t need Network Address Translation (NAT). Nowadays, computers have an address that allows them to connect to the internet with the same IP and access internal resources. Therefore, there is no need to separate the two networks with IP addressing. In fact, VoIP Quality of Service (QoS) is more potent as it makes connections to the PC possible.
- IPv6 transfers management of fragmentation to the device instead of the router. As a result, everything becomes much faster since there is no checksum handling.
- Rather than broadcast, IPv6 uses multicast. So, hosts that don’t follow your activities will not have to process the data packets.
- IPSec is now integrated with IPv6, which means your connections will be secure by default.
There is a common misconception that disabling IPv6 will reduce the attack surface. However, the truth is that IPv6 won’t leave your router if it doesn’t support it. On the other hand, if the router backs IPv6, it will protect your internal traffic by encrypting the header information.
How does IPv6 impact network traffic?
Since IPv6 does not use NAT, it doesn’t need a DHCP server, and the device will self-assign an address. It will query the network for a prefix and assign the rest automatically.
But, the problem here is a loss of control; you won’t see the addresses the machines are using.
Nonetheless, why do you need to care if the computers assign themselves and guarantee no duplication? Again, the problem is not the technology but the letting go of past practices.
Many IT admins are scared of not using NAT. It gives an illusion that the network is secure, yet devices connect to the internet in many ways. A device must either open a local firewall port or make the initial call to allow incoming traffic. Note that IPv6 does the same thing, except the router does not have to make the NAT calculations.
Currently, most networks still use DHCP servers and Group policy, but they’ll be eliminated eventually.
In addition, businesses no longer use digital keyphones, and their employees don’t work in brick-and-mortar offices anymore. It won’t be wrong to say that many companies have integrated some form of IoT into their networks. Even network-connected clocks and surveillance cameras count as IoT, and some businesses have gone further with more devices.
So, in short, networking has revolutionized, and the definition of ‘the edge’ has changed.
Probably you have heard that ‘the edge’ is a user credential. It is true today as employees can access corporate data remotely on devices like smartphones, laptops, tablets, etc. It shows how the edge is becoming transparent. For example, you can take your office desktop phone, plug in your home internet and make calls without requiring additional configuration.
The networking world is changing tremendously. Your network does not need DHCP, DNS, NAT scheme, or firewall for protection anymore. Instead, it is the credentials on that phone that matter. This is today’s edge, and that’s where security should be emphasized.
The drawbacks of IPv6 are fewer than the benefits. It’s more compact, agile, encrypted, and safer. However, more focus should be on modernizing legacy networking technologies to ensure that networks aren’t crippling. So, the best way to adopt IPv6 is to stop incapacitating it.
Conclusion
Undoubtedly, IPv6 is the future identifier for the internet. Nonetheless, until it gains enough privacy, security, and glitch-free functionalities, you may have to limit your device’s dependency on IPv6.
Thankfully, it is effortless to disable IPv6 through the network settings or Terminal commands regardless of your device. There is also an option to deactivate it on your router. So, you can use any of these options as temporary or permanent workarounds to stop IPv6 issues accordingly.